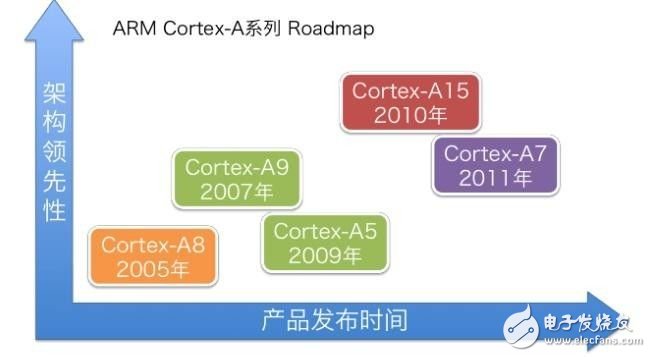
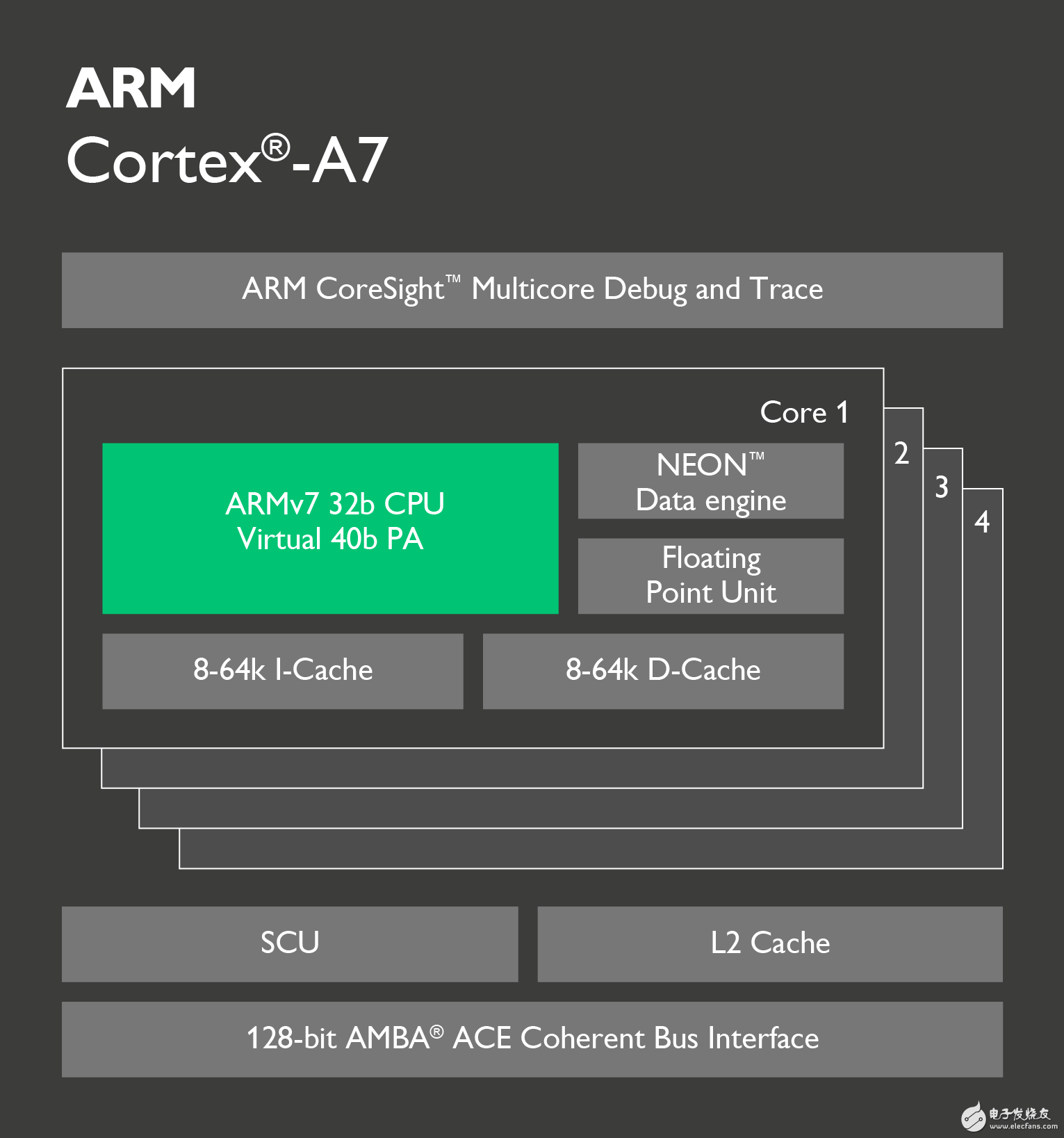
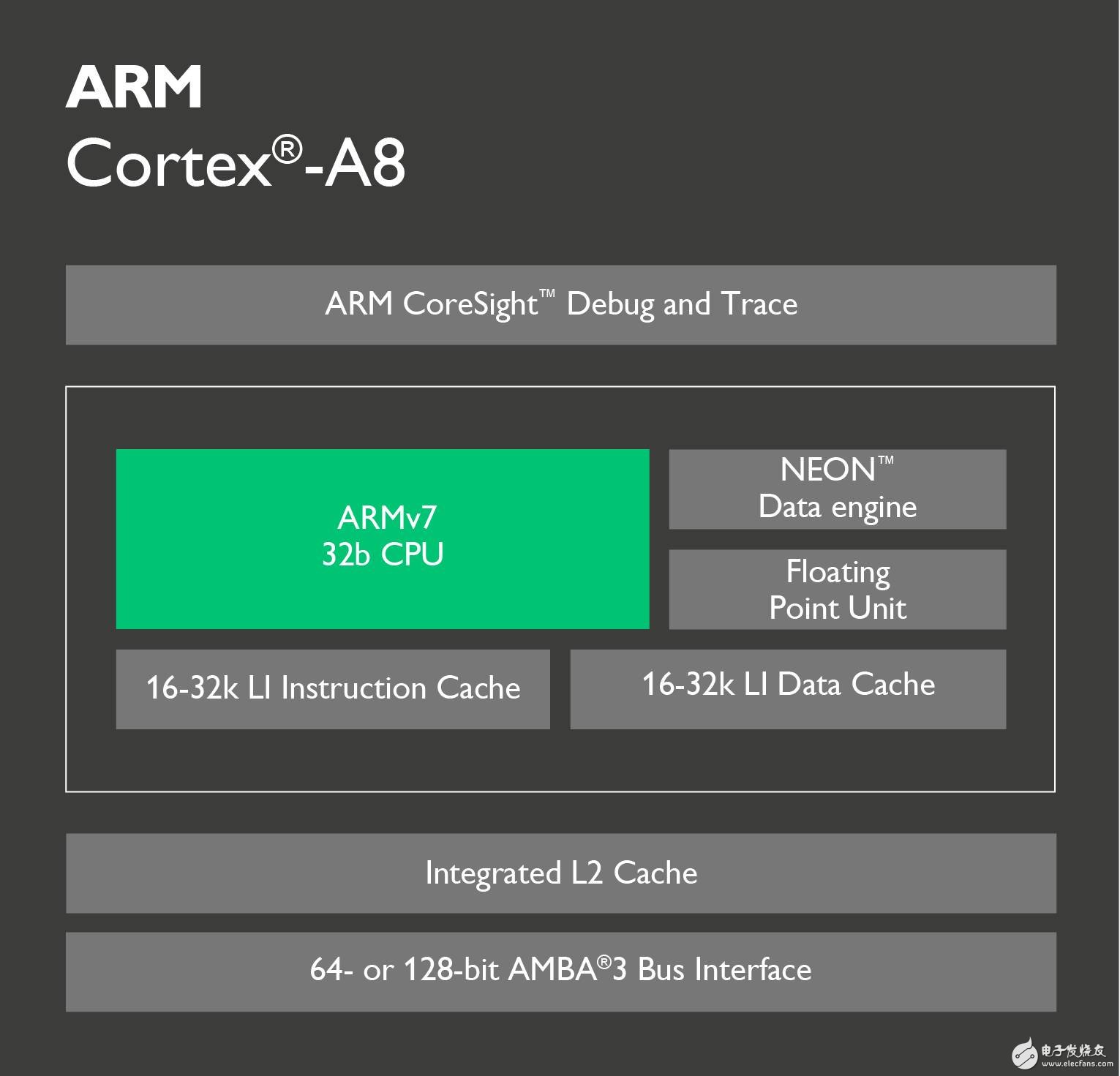
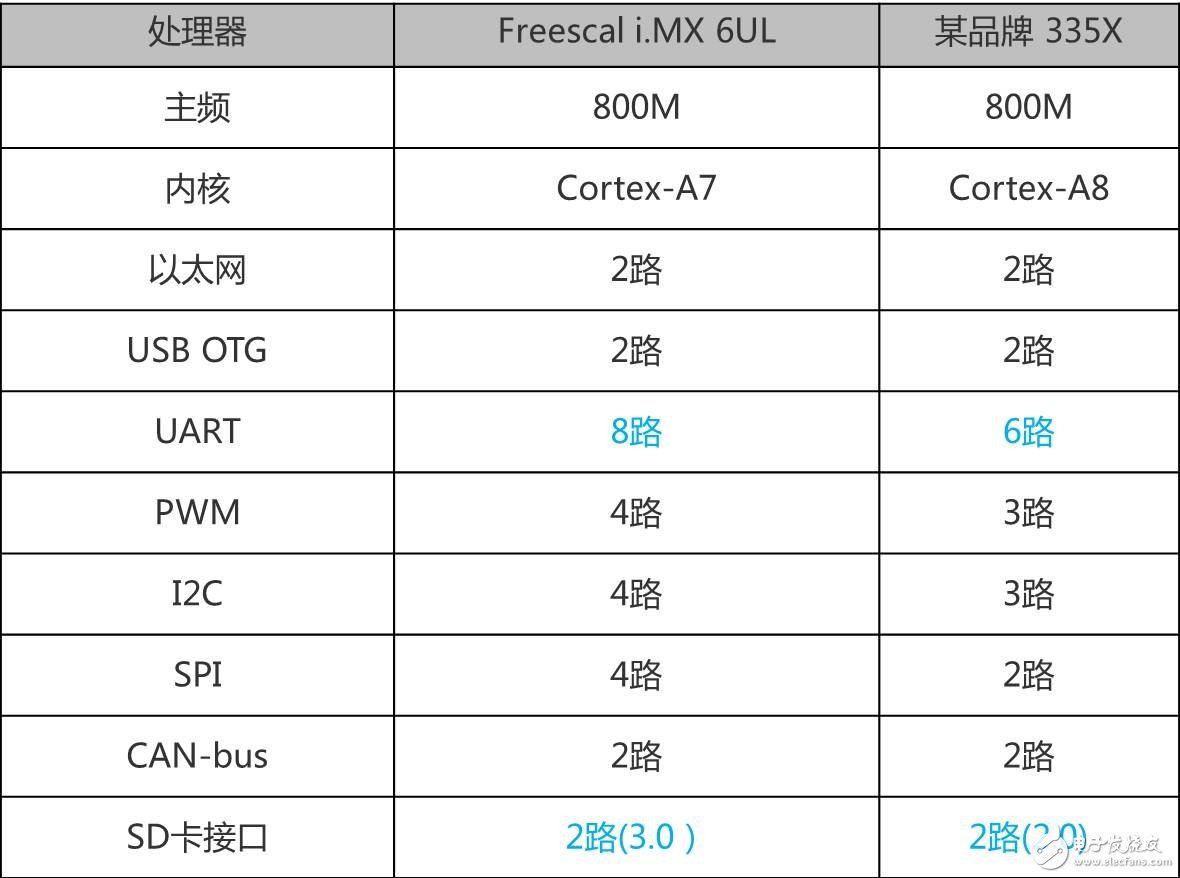
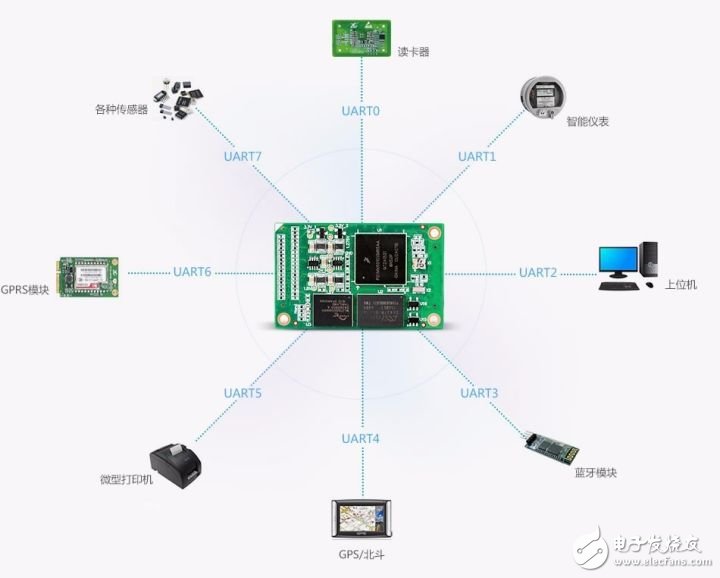
With the 800MHz clocked Cortex-A7 core MCU shocked, the early Cortex-A8 core MCU will face layer-by-layer strike, the same main frequency, lower power consumption, more exquisite manufacturing process, better quality and cost performance. The MCU market of the early Cortex-A8 core will face a huge impact, how should users choose? With the rapid development of the microelectronics industry, the core of the MCU is also developing rapidly. Engineers have also put forward higher functional and performance requirements for MCU selection. Embedded MCU selection is mainly based on performance and peripheral functions. Below we will mainly look at the difference between the performance and peripheral functions of the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8. Figure 1 ARM released kernel architecture time First, let's take a look at the release time of the ARM Cortex-A family of cores. We can see from Figure 1 that the Cortex-A8 was released very early, and it is the first Cortex-A series core of the ARMv7-A architecture; the Cortex-A7 was released later, which combines the advantages of the pre-release kernel. To make up for the shortcomings, there is a great increase in performance and functionality. Second, let's look at the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8 performance. The performance of the MCU is mainly based on the kernel architecture and manufacturing process. Let's take a look at the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8 core architecture diagrams. Figure 2 Cortex-A7 core The Cortex-A7 processor is an ARMv7-A-based energy-efficient processor from ARM that uses a 28nm/40nm manufacturing process to implement a single-core multi-core MCU. The processor is fully compatible with programs developed by other Cortex-A series processors and draws on the Cortex-A15 high-performance processor design including virtualization, Large Physical Address Extension (LPAE) NEON Advanced SIMD and AMBA 4 ACE New technologies such as consistency. The Cortex-A7 processor focuses on the balance between performance and power consumption. Figure 3 Cortex-A8 core The ARM Cortex-A8 processor was introduced to the market in 2005 as the first processor in the ARMv7-A architecture, using a 45nm/65nm manufacturing process. The Cortex-A8 can be used as a high-performance single-core processor for mobile consumer devices such as embedded devices, smartphones, netbooks, printers and a variety of other consumer devices. Since its introduction, the Cortex-A8 processor has been replaced by the Cortex-A15 and Cortex-A17 processors, but it represents a turning point in the high-performance 32-bit computing competition and is still widely deployed in many embedded applications. As can be seen from the above kernel architecture, the Cortex-A8 processor is the first processor of the ARMv7-A architecture and is a high-performance single-core processor. The Cortex-A7 is the MCU of the latest ARMv7-A architecture, and draws on the design of the Cortex-A15 high-performance processor, which greatly improves the performance. From the manufacturing process, the Cortex-A7 has a 28nm/40nm manufacturing process that is 45nm/65nm higher than the Cortex-A8. The Cortex-A7 has a great advantage in terms of power consumption. Finally, for the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8 cores, we chose the mainstream MCU on the market for simple peripheral interface comparison. We will compare the 800M clocked Cortex-A7 with the Cortex-A8 MCU, which are Freescal Cortex-A7 i.MX 6ULL ​​and a brand Cortex-A8 335X. Table 1 Comparison of peripheral interfaces Table 1 shows that the MCUs of the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8 cores are rich in peripheral interfaces. The MCU of the Cortex-A7 core refers to the MCU peripheral resources of the Cortex-A8 core, making the MCU of the Cortex-A7 core closer. Embedded applications, especially the 8-port serial design, greatly solve the need for multiple serial ports in industrial applications, and the design of high-speed SD card interface solves the problem of big data storage. ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics' M6Y2C is an industrial control core board that uses the Freescale Cortex-A7 800MHz processor to deliver lower power consumption with an advanced power management architecture. Standard 8-channel UART, 2-way USB OTG, 2-way CAN-Bus, 2-way Ethernet interface; standard 256MB DDR3 and 256MB NAND Flash, hardware watchdog; through strict EMC and high and low temperature testing, ensure the core board is in Stable work in a harsh environment. Figure 4 M6Y2C-256F256LI-T core board to sum up: Based on the analysis of the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A8 core architecture and manufacturing process, we can see that the Cortex-A7's low power consumption is particularly outstanding under the same performance conditions, which is in line with the current demand for embedded devices on the market. Through the comparison of the peripheral interfaces, we can see that the Cortex-A7 core has a rich MCU peripheral interface, which is in line with the current single-chip solution for embedded devices. According to the Cortex-A7 market, the MCU price of the Cortex-A7 core will be lower than that of the Cortex-A8 core. Therefore, the MCU entering the market in the Cortex-A7 core will have a great impact on the MCU market of the Cortex-A8 core. Will have a large market in the design of new products for customers. Active Stylus Pen,Stylus Pencil,Capacitive Stylus Pen,Tablet Pencil Shenzhen Ruidian Technology CO., Ltd , https://www.szwisonen.com