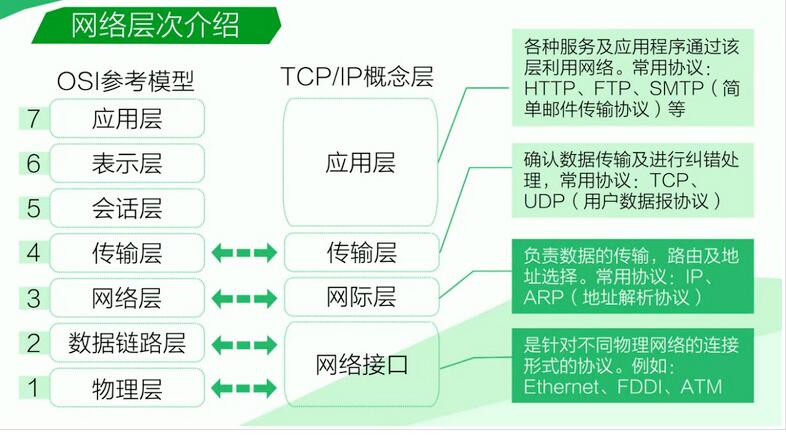
The reliability and redundancy of the network have been a topic that has not been discussed since the birth of the network. Recently, Alibaba Cloud released the cloud backbone network product, which has caused widespread discussion in the industry and suddenly felt that something happened in the WAN area. For example, the StartUP of SD-WAN based on Alibaba Cloud backbone is a good idea. When it comes to SD-WAN, it feels like it is a trade off between network reliability and construction cost, and of course there will be some flexibility. This article is mainly to share with everyone from the perspective of hierarchical HACK network, first with Xiao Bian together to understand what is the network layering. Network layering is to send or forward the data to be completed by the network node, package or unpack, control information loading or unloading, etc., and is completed by different hardware and software modules. This can simplify the complex issues of communication and network interconnection. Seven-layer model The OSI (Open System Interconnection) seven-layer network model, known as the open system interconnection reference model, is a logical definition and a specification that logically divides the network into seven layers. Each layer has related and corresponding physical devices such as routers (network layer) and switches (data link layer). The OSI seven-layer model is a framework design method. The main purpose of establishing a seven-layer model is to solve compatibility problems encountered when dissimilar networks are interconnected. Its main function is to help different types of hosts implement data transmission. . Its greatest advantage is to clearly separate the three concepts of services, interfaces, and protocols. Through seven hierarchical structural models, reliable communication between different networks in different systems is achieved. The main purpose of establishing a seven-layer model is to solve the compatibility problems encountered when heterogeneous networks are interconnected. Its biggest advantage is that the three concepts of services, interfaces, and protocols are clearly separated: The service describes what functions a layer provides for the upper layer, the interface describes how the lower layer of services is used by the upper layer, and the protocol involves how to implement This layer of services; so that each layer has a strong independence, what kind of protocol is used by each entity in the interconnection network is not limited, as long as the same service is provided upward and does not change the interface of the adjacent layer can be . The division of the network at the seventh floor is also for different functional modules (different levels) of the network to share different responsibilities. The benefits are as follows: 1, to reduce the complexity of the problem, once the network fails, you can quickly locate the level of the fault, easy to find and correct. 2. Define standard interfaces at each layer to enable different network devices with the same peer layer to achieve interoperability. Layers are relatively independent. A high-level protocol can be run on multiple low-level protocols. 3, can effectively stimulate network technology innovation, because each update can be carried out in a small range, without the need for the entire network surgery 1, the trench First of all, we discuss the negative layer of the network: the trenches, the general operators do network reliability protection requires the main and standby links can not be the same with the ditch, where the same ditch refers to this layer, do not underestimate On this level, this is the privilege of the party. It is not the one you want to dig. It is usually the most time-consuming layer. In this layer to see the reliability are generally local tyrants, such as we do metropolitan area network or long-distance WDM loop protection, digging at least two trenches between the two nodes, resulting in the cost is directly Double . As an ordinary user, what can be done at this level is limited and can even be ignored. 0X01 physical layer The physical layer here is mainly optical fiber. Fibers are placed in the trench, which is limited by the upper trench, so users can do similar things. 2, the data link layer Here take Ethernet as an example. From the beginning of HUB's working principle, it is broadcast directly (and of course the auxiliary CSMA/CD). It looks like a rough game, but it is also a more effective method in special scenarios. For example, in the field of telecommunications, some manufacturers, in order to meet the switching time of 50ms, are simply sending two packets of data directly to the core network through different paths to ensure low latency when switching. Individuals think this is also a broadcast. Application, of course, you can also say that this is a bandwidth-for-time approach. In the VR game field, in order to obtain real-time low latency, the screen information collected by the on-site camera, the position update of each backpack, and the information of the handle are all communicated via broadcast. Or one-to-many interoperability needs, on the other hand, is to increase the reliability of the network through broadcasting. Of course, the application scenario mentioned here may be that the network worker thinks this is a fuss and doesn't conform to the rules of the Internet. But I want to say who makes the business needs so wonderful. The network is already for the application service, only the white cat Black cats, cats that can catch mice are good cats. The main idea here is the idea. If you have such business needs, you can think in this direction. 3, the network layer The network is mainly IP. It is also the main battlefield of the network workers. Most of the network redundancy is implemented here. The dynamic routing protocols of the Cattle X are also used here. In addition to the master/backup or load redundancy technology implemented by the routing protocol itself, here are a few simple TIPs. For example, we all know that routing is a recursive query. Using recursion, we can solve some thorny problems. For example, some vendors' PBRs only support multiple next-hop loads or active and standby devices. We can recurse the next hop to static routes. Call the characteristics of the static route to implement related functions (load or active and standby or BFD detection, etc.). There is also a virtual next hop technology used in a similar backbone network of 163, which also uses recursive routing of routes to achieve network redundancy. There is the multiplexing of the upper layer to the lower layer. For example, multiple IP networks multiplex the same Ethernet network. Specifically, the port is a physical port configured to use multiple IP addresses, and the extension is to use the same Ethernet segment to use different IP addresses. Address network segment to meet specific needs. 4, the transport layer Here is the "class F5" of the world, through the front load balancing scheduling to achieve application-level network reliability. Of course, "class F5" has other functions. For example, everybody who plays Openstack knows that the floating IP implemented by the Neutron module only supports IP-level mapping between public and private networks, but we all know that IPv4 is very precious, especially in In the celestial state, the average company rarely had more than a few C-level addresses. But we can achieve port-level mapping by configuring load balancing in Horizon. Just add a Real Server to replace the intranet host. This is also a Trade off, and the risk is self-assessed. Row. Of course, the multiplexing of the transport layer to the network layer should be the reuse of the port level. The NAT mapping is a more widely used application, and this should be played by everyone. Various OVERLAY technologies are also used in this application. Most of them are UDP encapsulated IP or UDP direct encapsulated Ethernet (VXALN). This should be regarded as the multiplexing of the upper layer to the upper layer. Here, from the perspective of network layering, each layer can be Hacked technology, each layer can be used alone, can also be used in combination, such as the network layer can not solve the problem can be passed to the transport layer or data link layer, the physical layer can not be solved Problems can also be transferred to the network layer. Comcn Electronics Limited , http://www.comencnspeaker.com