At present, more and more household appliances are shifting from low-speed dial-up Internet access to broadband Internet access or Internet Protocol Television (IPTV), especially IPTV is expected to achieve rapid development in China. In comparison, the infrastructure cost of IPTV is quite low, because this method does not require a copper-axle cable, but uses DSL or broadband links and set-top boxes to stream the program to the home appliance. Figure 1: MIC37302 and discrete circuits ensure controlled slope and timing Tracking the power sequencing or power sequencing of the core and I/O power supplies adds complexity and cost to the power management circuitry. To overcome this problem, design engineers need a device that meets all of these needs without adding external components. An example of this product is Micrel's MIC68200 LDO for a variety of on-board power supply "target=_blank>LDO, which integrates rising speed control, power sequencing and tracking into a 3&TImes; 3mm MLF package . Figure 2: Tracking circuit, the ramp of the core voltage is set by the capacitor on the RC pin Figure 3: Sorting circuit, POR of the main regulator is enabled from the regulator, POR delay is set by low capacitance This Summary In summary, IPTV video broadcasting using FPGA coding and decoding platform as benefits are obvious. However, powering the FPGA can be a challenge, and the use of dedicated power management devices designed to meet power requirements, such as the MIC68200, will dramatically reduce time-to-market for new systems. Hydraulic High Pressure Sensor Hydraulic High Pressure Sensor,Thin Film Pressure Sensor,Vacuum Transducer,Brake Fluid Pressure Sensor Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com
Today's programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have proven to be ideal for such platforms because they provide the flexibility to quickly change market demands. The power requirements of an FPGA are often complex because FPGAs have up to three power requirements that must be ordered in order to achieve reliable system performance.
The core voltage core rail is typically set to VCCINT to power the FPGA logic. The required current ranges from a few hundred milliamps to tens of amps, depending on the clock frequency and the number of gates used. Because the load is highly capacitive, the core voltage and current requirements may be high at the beginning. The FPGA core has strict requirements for transient response, the core supply voltage must increase slowly and often requires a rise to a stable voltage for a fixed length of time. For example, Xilinx's Virtex-4 must power up the VCCINT supply between 0.2ms and 50ms.
I/O voltage
The I/O voltage (VCCIO) typically requires a voltage rail of 3.3V, 2.5V, 1.8V, or 1.5V. The I/O standard can be set independently by the I/O modules in the FPGA, so one FPGA may have more than one I/O voltage. The I/O current requirement depends on the number of I/Os used and the clock speed. Typically, I/O current requirements are low, ranging from a few hundred milliamps to 3A.
The auxiliary voltage auxiliary voltage (VCCAUX) requires the power supply to have a high power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) because the power supply is directly connected to Digital Clock Management (DCM). If power supply noise is allowed to couple to the DCM, it may affect the performance of the system.
Although I/O and auxiliary voltages do not need to be powered up in a particular order, FPGA manufacturers often specify the power-up sequence of the core and I/O or track the order. The consequences of not specifying the power-up sequence or not tracking the power-up sequence are often irreparable damage to devices in the system. FPGAs, PLDs, DSPs, and microprocessors typically place diodes between the core and the I/O supply as ESD protection components. If the power supply violates tracking requirements and exceeds the forward bias of the protection diode, the device may be damaged.
The solution is to illustrate the complexity of the FPGA power supply requirements, as an example of the VCCINT power-up requirements for a fixed period of time. In order to ensure the power-on time between 2ms and 50ms controlled by the upper and lower limits, the circuit shown in Figure 1 is implemented. 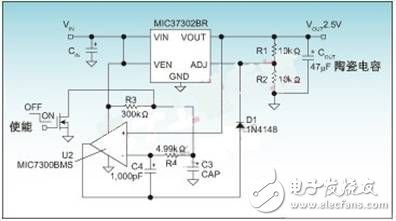
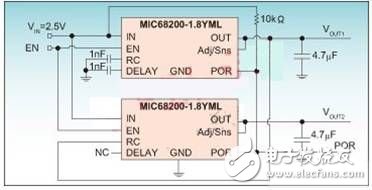
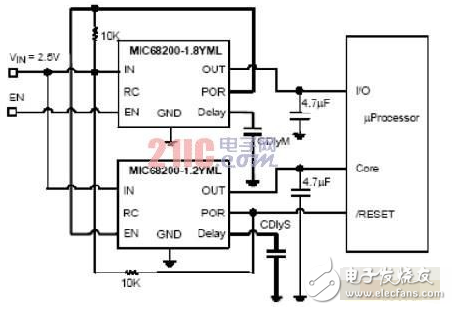
Multiple MIC68200s can be cascaded in two modes: In tracking mode, the output of the master drives the RC pin of the slave so that the slave tracks the main regulator during turn-on and turn-off; in sequential power-up mode, the master The POR of the device drives the enable (EN) terminal of the slave to turn on after the master is turned on and off before (or after) the master turns off. In addition to tracking capability, the Voltage Ramp Control (RC) pin accurately programs the ramp voltage of the core voltage rail with a single capacitor.
The tracking and sequencing circuits are shown in Figures 2 and 3, respectively. It can be seen from the figure that the solution is a simple implementation that requires few discrete components.